
Examples of Speech Synthesis in the Legal System
Discover how speech synthesis technology is revolutionizing the legal system with real-world examples.

When it comes to customer experience, companies are always looking for ways to improve it and ensure that they are delighting their customers at every stage. One way to do this is by creating a customer journey map.
In this article, we’ll discuss why customer journey mapping is so important, different elements that should be included when you create a customer journey map and how you can create your own customer journey map using it to understand the customer’s current state.
The customer journey is the path that a customer takes from becoming aware of your company to becoming a loyal advocate. A customer journey map helps businesses get a visualization of that path that helps companies to understand the various touchpoints that a customer has with their brand.
Mapping the customer journey is important because it helps companies to see where there are opportunities to improve the customer experience. It also helps to identify any pain points that customers may have so that those can be addressed. Additionally, mapping the customer journey can help to create more seamless customer experiences and make it easy for customers to do business with your company.
Customer experience describes the overall customer experience that the customer has with the brand. The brand must create visible experiences for potential customers throughout their Customer Journeys at every point in their journey. When purchases are positive, a positive experience is developed for customers. During this time, customer experience, and consumer needs are at the forefront. In a brand touchpoint, customer needs must be met.
Customers Journeys, Buyer Journeys, or Users Journeys are terms used to describe the stages of consumer experiences before buying a product. From the earliest details about an application to the purchase process, consumers can be divided into different stages.
Customer journeys involve the interaction between consumers and brands, products, or services. These routes could be tracked using customer journey maps. The consumer journey can vary by product and up to the point of the purchase decision and can last hours, weeks, or even months. The number of touchpoints can also range from many.
The customer journey includes all of the interactions that a customer has with a company, both online and offline. The user journey, on the other hand, focuses solely on the online experience. Additionally, the customer journey takes into account the entire purchase cycle, from awareness to purchase to post-purchase, while the user journey focuses only on the purchase itself.
Customer journey mapping is the activity of making a customer journey map. This map is simply a visual illustration of what a company’s customers experience as they interact with the business. All gathered information from various touchpoints is compiled into one place to get an overview of the customer’s entire experience.
Customers have a set path through your business. That’s why understanding the relationship between all their touchpoints is important for making sure you’re creating an effective process that leads them to where they want or need to go.
The model is different and can be adapted to different customers. They all divide the customer journey stages into different phases. In each stage, customers have different requirements or want different things. If companies respond to this request in the right way, they can be able to improve the customer experience and ultimately connect the customer to the company.
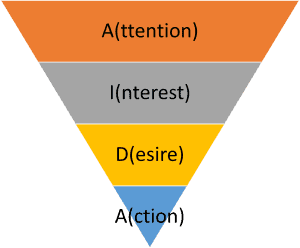
The classic customer journey is broken down into a five-phase system: The 5-phase model expands further to AIDA’s famous goal-oriented AIDA model: attention-inspiration.
Awareness: The customer becomes aware of the problem or need.
Interest: The customer develops an interest in a solution to the problem or need.
Desire: The customer really wants the product or service that will solve the problem.
Action: The customer takes action and buys the product or service.
Loyalty: The customer continues to use and buy from the company, becoming a loyal fan and promoter.

It is possible to present different types of customer journey that have changed over time. This model is a methodological model aimed at presenting customer experiences, often quite individual. Unstructured Customer Journeys: a practical model. They usually follow linear or cyclical approaches.
It is possible to present different types of customer journey that have changed over time. This model is a methodological model aimed at presenting customer experiences, often quite individual. Unstructured Customer Journeys: a practical model. They usually follow linear or cyclical approaches.
The concept of the Messy Middle assumes that the user still goes through studies and evaluations before deciding whether to buy. When looking at a product, service or other products, the customer usually follows a specific order. Based on where users are, they want to buy knowledge, then solutions, or finally a specific product or solution. Using triggers, users enter research processes at different points in the user journey, depending on their level of knowledge about the product or service. Google describes the process as changing the way they consider before making a purchase.
Moments of Truth is an extremely popular customer journey model. It gives you an overview of how your customer’s mindset can change as they experience different touchpoints in their Customer Journey. The model is based on the idea that each customer touchpoint is a Moment of Truth, where the customer’s attitude can change.
A positive experience at a touchpoint can lead to a positive change in the customer’s attitude. A negative touchpoint, on the other hand, can cause the customer’s attitude to change negatively. According to the model, each touchpoint in the customer journey is an opportunity to improve or worsen the customer’s attitude.
It is important for companies to know at which touchpoints the customer’s attitude may change so that they can take appropriate action to ensure a positive experience.
The consumer journey is based on a McKinsey project. The model is not a “tunnel.” The process begins in the review phase before the AIDA model is completed. The customer needs solutions limited to existing products and brands. It then analyzes what it wants to do and analyzes what it can offer. The user ultimately decides to buy the specific solution. The user-client relationship is now customer-centric.
AIDA follows a 4-step customer journey. This AIDA model has four stages: AIDA models describe the first three phases: the target audience and the initial purchase decision.
The AIDA model (Awareness, Interest, Desire, Action) is a classic among the customer journey models.
There are no specific shapes that show the customer journey. Instead, the entire package should clearly and holistically encompass all the things summarized here. It aims to ensure that anyone using customer journey maps can figure out exactly what is important in a given situation.
Customer journey maps should include the following:
The customer journey map is a way to think about the entire buying process in terms of stages. Each stage will be represented by one horizontal bar on your representation, and you’ll use these bars as guides when developing specific content for each section that covers people’s needs at different points throughout their purchase lives (such as first-time buyers).
This element would allow you to dive into the details of each stage. For each stage, you’ll need to think about what your customers are trying to achieve and what their needs are.
The customer journey map explores what a customer does in each stage of the buying process. In the awareness stage, they might speak with friends and family about their needs and compare ways to satisfy those needs. Eventually, they take a demo on your website before making their purchase.
Thus, the customer journey map would look something like this:
Emotion is an element that should be included in your customer journey map. Customers experience a wide range of emotions throughout their journey, from excitement to frustration. Understanding how your customers feel at each stage of their journey can help you optimize their experience.
For example, a customer who is just beginning their research may be feeling excited about the potential purchase. However, a customer who has been researching for a while and still can’t find what they’re looking for may be feeling frustrated. If you can identify when your customers are feeling frustrated, you can take steps to prevent them from becoming discouraged and giving up on their purchase altogether.
This element comes in when your customer is further into their journey and encounters problems or pain points. It’s important to understand what these pain points are so that you can take steps to address them.
Pain points in the customer journey are typically caused by:
If you can identify and address these pain points, you’ll be well on your way to providing an excellent customer experience.
With these obstacles you have identified, it is now time to provide solutions. These solutions will help to reduce or remove the pain points that your customers are experiencing.
Some solutions you can provide are:

As touched on earlier, a touchpoint is any interaction your customer has with your brand – whether it’s digital or physical. In order to create an effective customer journey map, you’ll need to identify all of the touchpoints in your customer’s experience.
Some examples of touchpoints include:
In-person visit
There are endless possibilities when it comes to touchpoints, and the number of touchpoints will vary depending on your business. Once you’ve identified all of the touchpoints in your customer’s experience, you can start mapping out their journey.
It’s crucial to take into account all the different types of touchpoints beyond just your website and marketing materials when mapping out your customer journey. This will help you see potential areas where you can improve the buyer’s experience.
You can create a customer journey map by plotting out all of the touchpoints in your customer’s experience. You can use a simple sheet of paper or whiteboard to do this, or you can create a digital version using some tool.
With the key elements in place, you can now have a good overview of your customer’s journey. Identifying potential areas for improvement should be your next step. Once you’ve done that, you can start to work on making changes to improve the customer’s experience.
What do you want to learn from it? What changes do you want to make based on what you learn? By having specific goals in mind, you can ensure that your customer journey map is effective and helps you meet your objectives.
In order to better represent and serve your customers, you may want to create a buyer persona. This is an ideal customer with all of their demographics and psychographics who represents your average customer. Having a clear persona is helpful in reminding you not to forget anyone as you journey map out the steps they take towards becoming your loyal paying customer.
The only people whose feedback you want are those who have or plan to actually buy your products and services.
These are the people you want to focus on.
Creating customer journey maps can be done in a number of ways, but there are some basics that should always be included:
– who your customer is
– what their goal is
– what pain points or challenges they face along the way
– what type of interactions do they have with your brand
– what emotions they feel throughout their journey
By doing this, you can develop messaging that will be more resonant and effective. For example, if you know that your target market is busy moms, you can create messaging that speaks to their need for time-saving solutions.
Identify the steps they take on their journey.
Be as specific as possible, and include both digital and offline touchpoints. For example, if you’re a brick-and-mortar retailer, your customer’s journey might include steps like:
– Seeing an ad for your store in a magazine
– Visiting your website
– Stopping by your store
– Making a purchase
– Leaving a review on your website or social media
Creating a customer journey map can seem daunting, but it doesn’t have to be. There are a few different ways to approach it. You can start with a list of all the touchpoints your customer has with your brand, both online and offline. Once you have that, you can start to map out the journey, identifying which touchpoints are most important at each stage.
Then, you should start to group them together by stage. For example, all the touchpoints that happen before a purchase would be grouped together, as would all the touchpoints that happen after a purchase.
Once you have your customer journey stages and touchpoints mapped out, you can start to add more detail. This is where you’ll want to think about the customer’s needs at each stage, what they’re trying to achieve, and what you want them to do.
You should also consider what kind of experience you want your customers to have. This will help you to identify any gaps in the journey and make sure that every touchpoint is delivering on your brand promise.
Finally, you’ll want to map out the channels that your customers are using at each stage. This will ensure that you’re delivering a consistent experience across all touchpoints.
This will largely be determined by your goals for the map. For example, if you’re trying to improve customer satisfaction, you may want to include measures of satisfaction at each stage.
If you’re trying to increase sales, you’ll want to track conversion rates. And if you’re trying to reduce support costs, you’ll want to track the number of support requests at each stage.
Once you’ve determined what elements you want to track, it’s time to start mapping out the customer journey. You can use a variety of different methods to do this, but we recommend starting with a simple spreadsheet.
In the first column, list out all of the stages in the customer journey. In the second column, list out the key actions that customers take at each stage. And in the third column, list out the key measures you want to track.
This will help you understand what’s working well and where there are gaps. Identifying the resources you need will help you fill in those gaps.
Common resources you might want to include are:
– Customer data
– Employee data
– Sales data
– Marketing data
– Social media data
– Website analytics data
But don’t feel like you need to limit yourself to just these sources. Any data that can help you understand your customers’ journey is fair game.
Once you have all of your data, it’s time to start mapping out the journey. The best way to do this is to create a customer journey map.
Having personal experience with your product or service is always going to give you the best insight into how your customers experience it. If you can’t use your product or service yourself, talk to someone who can.
Your goal here is to understand the customer’s needs, wants, and pain points at each stage of their journey. By doing this, you’ll be able to identify areas where you can improve the customer experience because you experienced it firsthand.
Now that you have a better understanding of how your customers interact with your product or service, it’s time to make some changes. This is where you’ll take the insights you gained from your customer journey map and turn them into concrete actions.
Some changes will be small, like tweaking the copy on your website. Others will be more substantial, like redesigning your entire checkout process. But no matter how big or small the changes are, they should all be aimed at making the customer experience better.
Describe how customers travel to and from their target audience. The buyer’s journey has 2 basic approaches. During the Sales Funnel, the Customer Journey goes far beyond and follows up with the existing customer. Client Tour models can usually come in vertical or horizontal models.
By identifying each stage of their journey, you can begin to see what content, message, and offer are best suited for that particular stage.
The goal of customer mapping is to reduce the risk of your target audience churning or becoming uninterested and subsequently improve customer retention rates. Creating a customer map will also help you to better understand how your target audience interacts with your brand, what their needs and wants are, and how you can better serve them.
The Customer Journey is more complicated and linear as technology advances. At each stage, the potential customer passes through different touchpoints, e.g. Facebook, Twitter, or Amazon, until the subsequent positive experience makes them the most loyal. A mapping solution reduces the complexity of customer journeys by visually representing a complete customer journey using customer journey maps. Provides an overview of how to analyze the customer experience.
A customer journey map is a great way to get insights into how your customers interact with your brand. By mapping out the customer journey, you can identify areas where there are opportunities to improve the customer experience. You can also use customer journey maps to create more personalized experiences for your customers.
If you want help creating a customer journey map for your business, get in touch. We’d be happy to help you create a custom map that meets your specific needs.



Discover how speech synthesis technology is revolutionizing the legal system with real-world examples.

Explore how speech synthesis technology is revolutionizing the agricultural industry with real-world examples and applications.
Explore how speech synthesis technology is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry with real-world examples.
